Enhancing Senior Behavioral Health in Assisted Living
Senior behavioral health is a crucial element of overall well-being in assisted living environments like Westmont of Morgan Hill. As seniors navigate the complexities of aging, their emotional and cognitive health becomes just as important as their physical care. Whether managing new diagnoses or adapting to lifestyle changes, mental and behavioral health support must be intentional, compassionate, and tailored to individual needs.
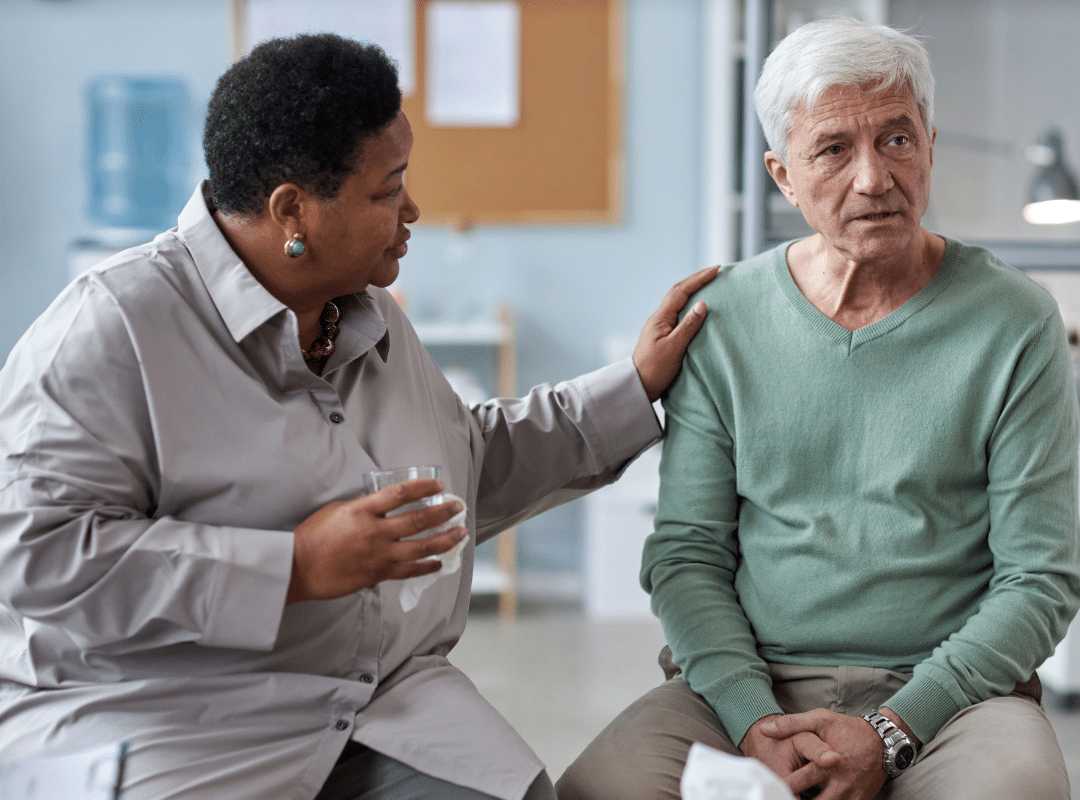
Seniors in assisted living often face unique challenges—social isolation, cognitive decline, and the grief of losing loved ones. These factors can amplify mental health concerns, making it critical to provide consistent emotional and psychological support. At Westmont of Morgan Hill, we prioritize structured routines, therapeutic activities, and family involvement to foster emotional balance and meaningful connections.
Understanding Senior Behavioral Health Challenges
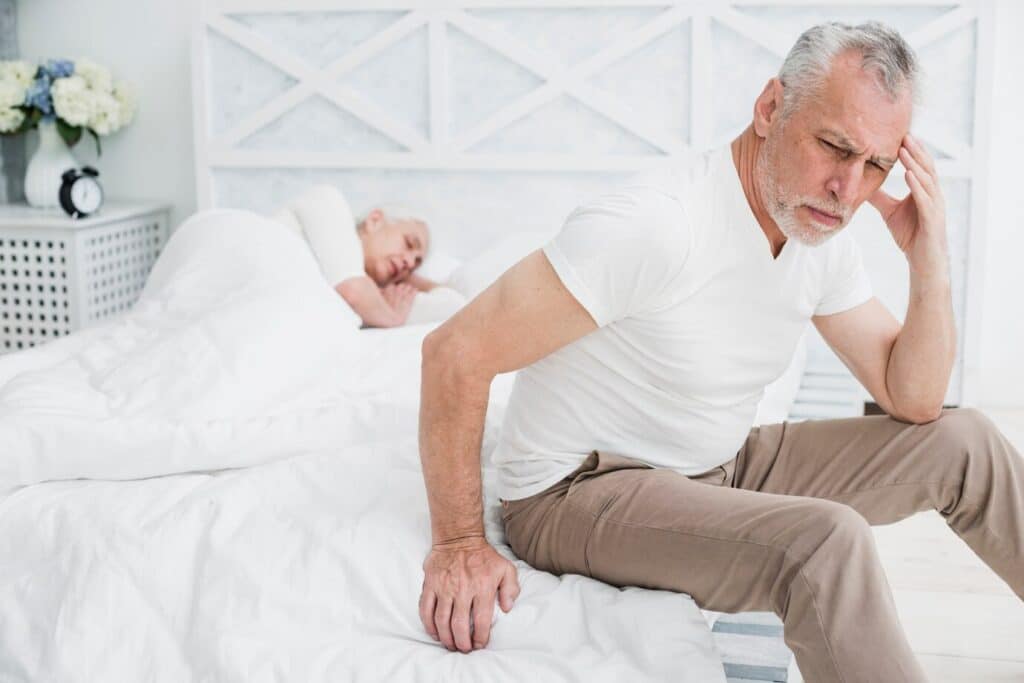
Senior behavioral health is impacted by a range of life transitions. Aging adults commonly experience cognitive impairments, grief, and physical limitations that contribute to emotional distress. These challenges can cause behavioral shifts such as withdrawal, aggression, or confusion, which are often misinterpreted as simply “part of aging.” However, they may signal more serious conditions that require intervention.
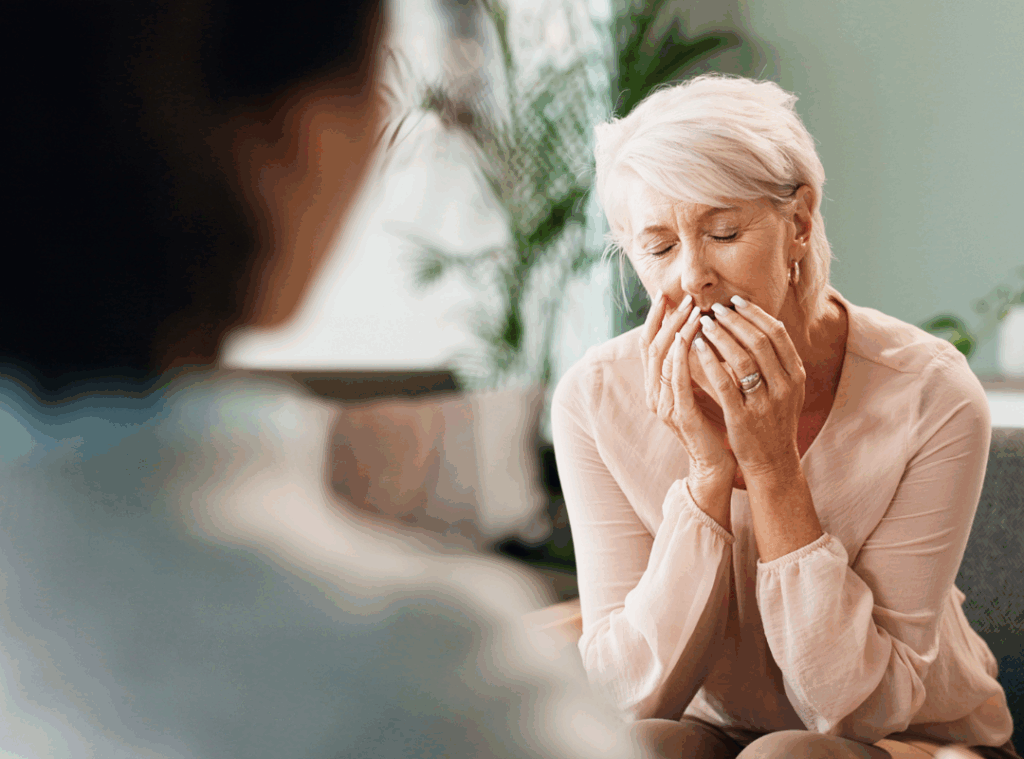
When considering what is the most common mental illness in the elderly, depression tops the list. Studies show that depression affects up to 20% of seniors in assisted living facilities. Left untreated, it can severely impact quality of life. Other illnesses include anxiety, bipolar disorder, and dementia-related conditions, forming the four common mental illnesses in the elderly.
That’s why we take a holistic approach to care that includes both clinical evaluations and personalized emotional support. This model is further explored in our blog post on Seniors and Mental Health, which debunks common myths and highlights practical tools for intervention.
Identifying and Managing Common Mental Illnesses in the Elderly
Understanding and recognizing the four common mental illnesses in the elderly—depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and neurocognitive disorders like dementia—is essential. Knowing how to deal with mental illness in elderly loved ones means first being able to identify warning signs such as sleep disturbances, mood swings, or lack of interest in favorite activities.
Each condition affects seniors differently. For example:
- Depression often presents as fatigue or irritability, rather than sadness.
- Anxiety may center around fears of falling, illness, or being a burden.
- Bipolar disorder can be triggered by medication changes or chronic illness.
- Dementia brings behavioral challenges that require memory care expertise.
Proactive screening and intervention can make a profound difference. This article from the CDC outlines valuable insights into the prevalence and impact of mental illness in older adults.
How to Improve Mental Health in Elderly Residents
Knowing how to improve mental health in elderly individuals starts with daily routines that foster purpose and connection. At Westmont of Morgan Hill, we employ structured activities and therapy programs designed to encourage emotional resilience.
Some effective strategies include:
- Mindfulness and breathing exercises to manage stress
- Group therapy sessions to address grief and anxiety
- Art and music therapy for emotional expression
- Cognitive stimulation through games and discussion
We also encourage family members to participate in these activities, strengthening relationships and reducing the emotional distance that can develop over time.
To learn more about the importance of targeted emotional care, visit our resource on Anxiety in Older Adults.
Building Emotional Strength Through Connection
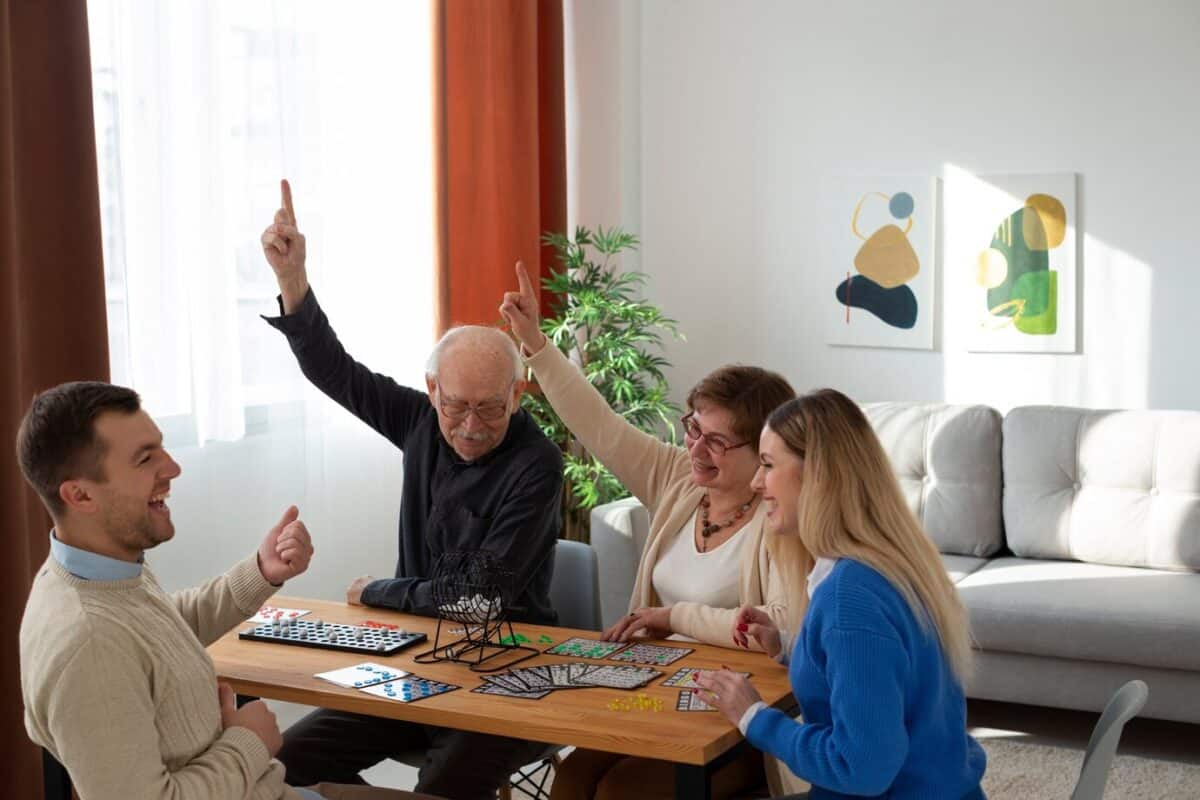
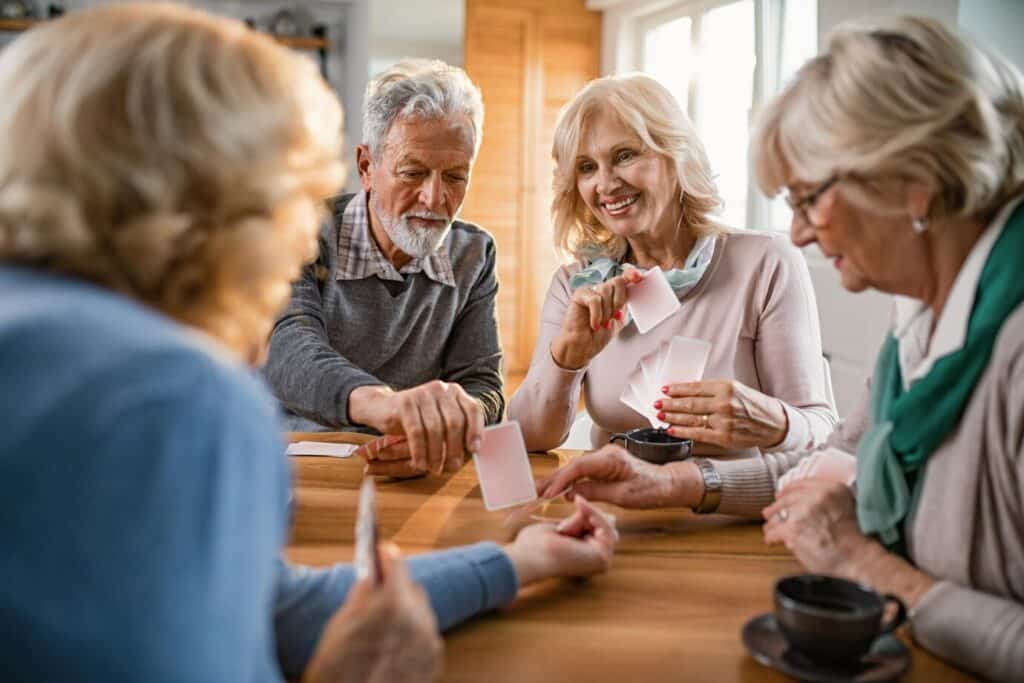
Isolation is one of the greatest threats to senior behavioral health. That’s why community-building and personal engagement are at the core of our programs. Regular social interaction not only improves mood but also enhances memory retention and self-esteem.
To counteract isolation, we promote:
- Resident social groups
- Daily communal meals
- Collaborative creative workshops
- Outdoor group activities and nature walks
When seniors feel seen and valued, they thrive. These connections are especially crucial for residents with mental health concerns, offering both distraction and emotional nourishment.

The Role of Families and Caregivers
Families play a pivotal role in supporting senior behavioral health. Maintaining open communication, sharing medical updates, and encouraging participation in activities all contribute to emotional stability.
Here’s how families can support loved ones:
- Recognize how to deal with mental illness in elderly relatives by staying informed and compassionate
- Understand what the most common mental illness is in the elderly, so they know what to expect
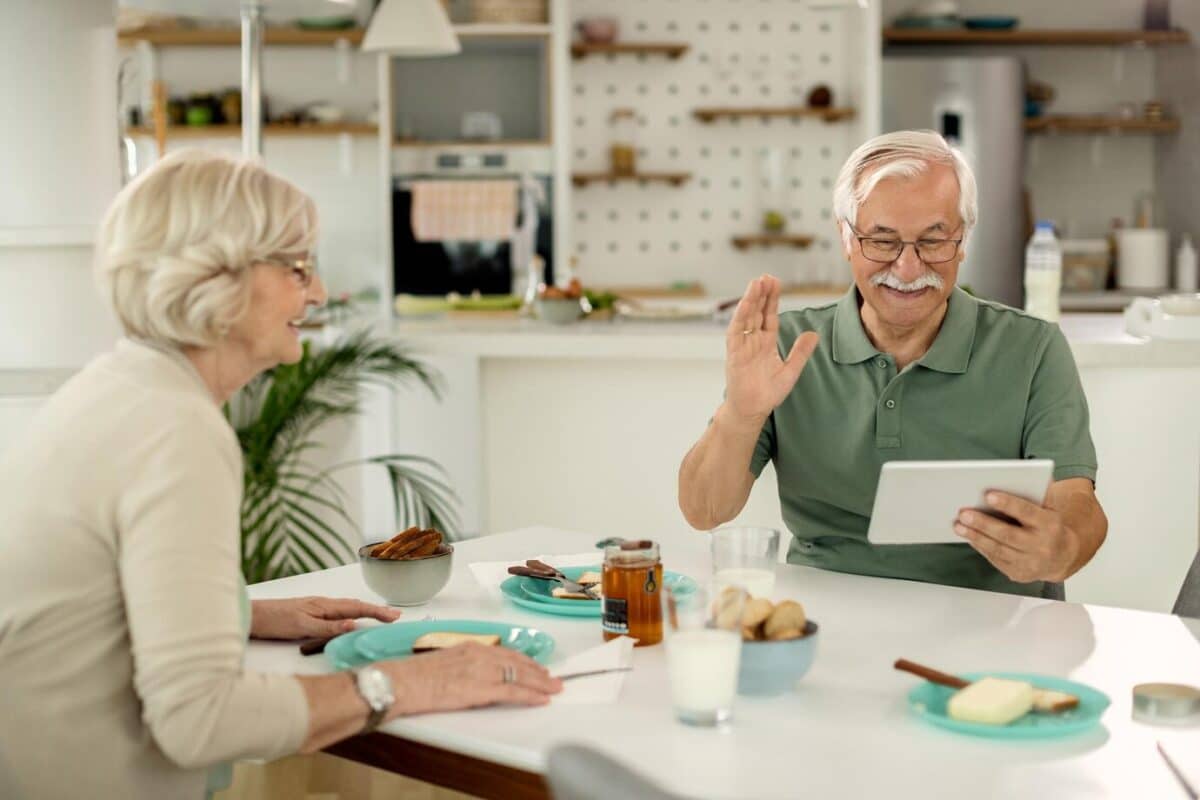
- Use technology (video calls, photo sharing) to bridge long-distance gaps
- Participate in family engagement programs designed to build stronger bonds
Caregivers also need support. Those tending to seniors with behavioral challenges are at risk of burnout. That’s why we encourage them to adopt self-care practices, join peer groups, and access respite care when needed.
Creating Safe and Stimulating Environments
Environmental design plays an underrated but critical role in senior behavioral health. Safe, accessible, and welcoming spaces reduce anxiety and confusion, particularly for residents with dementia or bipolar disorder.
Here are a few ways we ensure our facility promotes mental well-being:
- Clearly marked hallways and doors to reduce disorientation.
- Soft lighting and natural views for mood stabilization.
- Private quiet areas for meditation or one-on-one therapy.
- Outdoor walking paths encourage light exercise and relaxation.
All these elements work together to create an environment that is not only safe but uplifting—a place where residents feel comfortable expressing themselves.
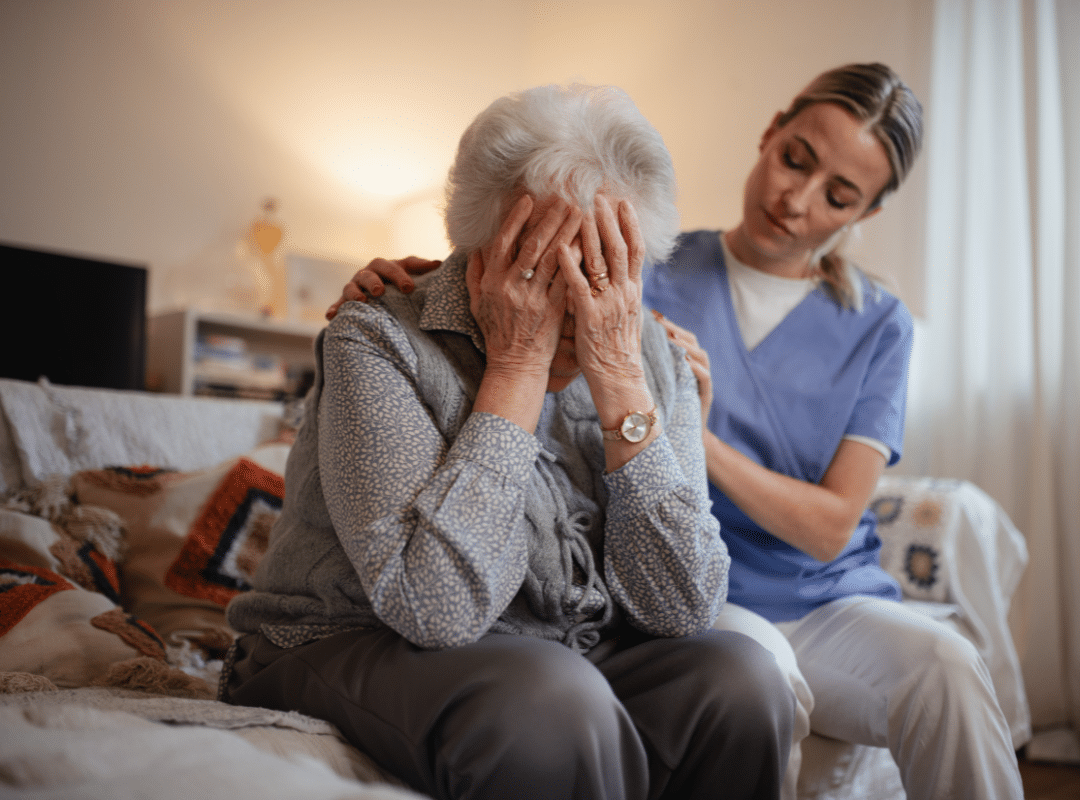
Compassionate Care at End-of-Life
Behavioral health remains a top priority even in palliative care stages. Seniors facing end-of-life transitions often experience increased anxiety, grief, or existential fear. Facilitating thoughtful discussions about legacy, wishes, and meaning can help ease emotional distress.
We train our staff to:
- Provide non-judgmental listening.
- Encourage journaling, prayer, or storytelling.
- Offer spiritual counseling when desired.
- Involve family in memory-sharing rituals.
A peaceful, emotionally supported transition preserves dignity and provides closure for both residents and families.
Community and External Resources for Support
Many tools and resources, beyond those at Westmont of Morgan Hill, support senior behavioral health. These include:
- National Institute on Aging: Offers research and tips on managing depression in seniors
- Mental Health America: Provides assessments, treatment options, and caregiver support
- Local community senior centers: Often provide free therapy, exercise classes, and peer engagement
Combining facility-based care with community outreach can dramatically improve outcomes for elderly residents.
Championing Emotional Wellness in Senior Living
Caring for senior behavioral health isn’t just about managing symptoms—it’s about preserving dignity, identity, and joy. Whether you’re a caregiver, family member, or assisted living professional, your role in supporting mental wellness is powerful.
If you’re wondering how to improve mental health in elderly individuals or struggling with how to deal with mental illness in elderly loved ones, know that help and resources are always available. Compassionate support, community engagement, and proactive care can make all the difference.
To see how Westmont of Morgan Hill champions this mission, schedule a tour or contact us directly at 408-779-8490. Let’s work together to ensure that every senior experiences a life filled with purpose, connection, and peace.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to deal with mental health in the elderly?
Supporting elderly mental health involves encouraging regular social interaction, physical activity, and routine medical checkups. It’s important to create a safe, understanding environment where they can express emotions freely. Professional counseling, support groups, and medications can also be beneficial when needed. Family involvement plays a crucial role in reducing isolation and promoting emotional well-being.
What is an example of Behavioural health?
An example of behavioral health is managing depression through therapy and lifestyle changes such as exercise and mindfulness. It includes the connection between behavior, mental well-being, and physical health. Substance abuse treatment and stress management are also key components of behavioral health care. It addresses both mental illnesses and the habits that affect overall well-being.
What is the mental health of senior citizens?
The mental health of senior citizens refers to their emotional, psychological, and social well-being as they age. Common concerns include loneliness, cognitive decline, depression, and anxiety. Good mental health helps seniors enjoy life, maintain independence, and handle daily stressors. Proper care involves medical support, companionship, and engaging activities that keep the mind active.
What is the most common mental health issue in older adults?
Depression is the most common mental health issue among older adults. It often goes undiagnosed because its symptoms can be mistaken for normal signs of aging or physical illness. Depression in seniors can lead to decreased quality of life and increased risk of physical health problems. Early detection and treatment through therapy, medication, or social engagement can significantly improve outcomes.