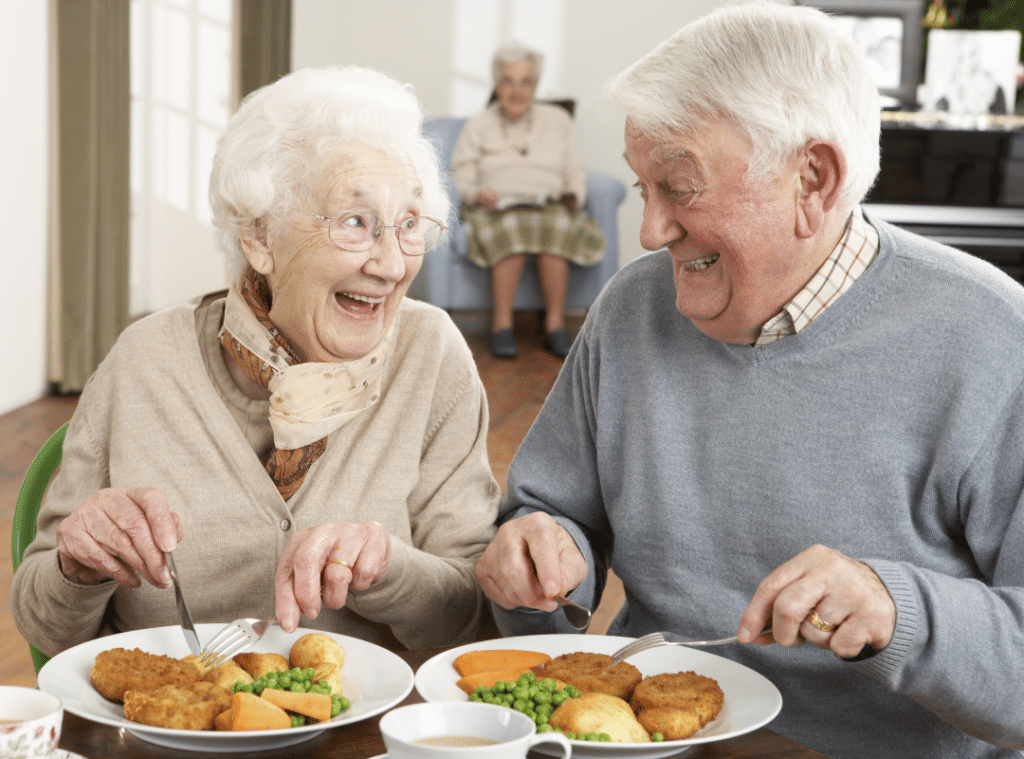
Maintaining proper nutrition becomes more challenging with age, and knowing how to improve appetite in the elderly is crucial to supporting their overall health and quality of life. With changing tastes, decreased energy, and various medical conditions, it’s no surprise that many seniors struggle to maintain healthy eating habits.
Whether you’re a caregiver or a loved one seeking to help, there are natural and effective methods to stimulate appetite and ensure seniors receive the nutrients they need. In this guide, we’ll explore causes, practical solutions, and the importance of social engagement and support systems in boosting the elderly’s appetite.
For hands-on help and guidance, visit Westmont of Brentwood. Let’s dive into the details.
Understanding Appetite Changes in Seniors
As adults age, several physiological changes begin to affect hunger and food intake. A weakened sense of taste and smell can dull food enjoyment, and reduced physical activity often means fewer hunger signals. Understanding how to increase appetite in the elderly naturally begins with recognizing these natural shifts.
Oral health problems, medication side effects, and underlying conditions like arthritis or diabetes can further decrease appetite. Additionally, poor hydration—often overlooked—can exacerbate the issue. Encourage regular fluid intake and nutrient-rich snacks to counter these challenges. Learn more from this post on why elderly people stop eating.
Identifying Underlying Causes of Appetite Loss
Before implementing solutions, it’s vital to pinpoint the root causes. Is the issue physical, emotional, or both? This step can guide personalized care that leads to lasting improvements.
Common Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like cancer, dementia, thyroid disorders, and gastrointestinal issues can lead to significant appetite loss. One proven treatment for loss of appetite in the elderly includes modifying medications or adjusting diet to suit individual needs.
Often, the medications seniors rely on for these illnesses cause nausea or fatigue, further impacting food intake. Work closely with a healthcare provider to review prescriptions and ensure they aren’t doing more harm than good.
Explore how chronic conditions play a role in senior health here: chronic conditions.
Psychological Factors Impacting Appetite
Mental health is often the silent culprit. Depression, anxiety, grief, and isolation are leading causes of appetite suppression. Cognitive decline can interfere with recognizing hunger or remembering to eat. Caregivers must observe emotional changes and provide mental health support alongside nutritional care.
Check this article to learn how nutrition supports mental health in aging: supporting seniors with dementia.
| Psychological Factor | Impact on Appetite |
| Depression | Decreased interest in food |
| Loneliness | Reduced motivation to eat |
| Cognitive Decline | Missed hunger signals |
| Anxiety | Nausea during meals |
Practical Strategies to Stimulate Appetite
There are simple ways to make meals more enjoyable and inviting. Start with visual appeal—plate food in vibrant, colorful ways. Use aromatic herbs and spices to stimulate taste and smell.
Consider offering finger foods like fruit slices or mini sandwiches to reduce mealtime stress. Regular eating schedules and social mealtime settings can significantly help seniors feel hungry at appropriate times.
Small, frequent meals are key. This approach ensures nutrient intake without overwhelming the digestive system.
Nutrient-rich options can be found here: appetite-enhancing tips.
Top Recommendations
- Offer food for the elderly with no appetite, like Greek yogurt, protein smoothies, and soft fruits.
- Try flavor-enhancing herbs instead of heavy salt or sugar.
- Introduce supplements to increase appetite in the elderly if a nutrient deficiency is suspected.
- Keep high-calorie, low-volume snacks available, like trail mix or cheese cubes.
- Serve meals with warm soups or herbal teas to stimulate digestion.
If you’re unsure where to begin, the National Institute on Aging offers excellent resources on healthy eating habits for seniors.
Nutritional Options for Enhanced Intake
The goal isn’t just more food—it’s better food. Think about how to increase appetite in the elderly naturally by offering appealing and nutrient-dense foods.
Consider these ideas:
- Meal Fortification: Add healthy fats like avocado or olive oil to meals.
- Easy-to-Eat Snacks: Nut butters, applesauce, and pudding can offer needed calories.
- Smoothies & Soups: Ideal for hydration and nutrient intake, particularly beneficial for seniors with chewing difficulties.
- Hydration Solutions: Offer beverages like coconut water or electrolyte drinks for variety and function.
The Role of Social Interaction in Eating
Meals are more than nutrition—they’re an emotional and social experience. Loneliness is a leading factor in appetite loss. Shared meals with friends or family foster a positive association with food.
Encouraging Group Meals
Group dining encourages conversation, creates structure, and improves emotional well-being. Facilities like Westmont of Brentwood incorporate social dining into their daily routines for this very reason.
| Benefit | Description | Evidence |
| Social Connection | Fights loneliness | Research-based outcomes |
| Appetite Stimulation | Mealtimes become events | Positive feedback |
| Nutritional Balance | Meals are supervised and balanced | Institutional practices |
Enhancing Dining Atmosphere
Create a sensory-rich environment. Dim lighting, soft music, and cozy seating can do wonders for mealtime enjoyment. Serve meals on brightly colored plates to improve visibility and interest.
Engaging Activities and Hobbies
Involving seniors in cooking or gardening can give them a sense of purpose, which indirectly improves their appetite. Activities like painting, music sessions, and puzzle games stimulate the brain and boost mood, creating a healthy environment for eating.
Supplements and Medical Aids
When natural methods aren’t enough, supplements to increase appetite in the elderly may be recommended by a physician. Options include multivitamins, zinc, and medical-grade meal replacement shakes.
Be sure to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement plan. These products can interact with existing medications or conditions.
Support Services and Care Options for Seniors
Professional care options can make all the difference. Westmont of Brentwood offers tailored dining experiences, professional meal planning, and engaging social programs that promote nutritional health.
Options include:
- Senior Living Facilities: Structured environments with health monitoring
- Respite Care: Temporary support to give caregivers a break
- In-Home Aides: Help with meals, grocery shopping, and feeding assistance
- Nutritional Counseling: Personalized meal plans and appetite assessments
If you’re struggling with how to improve appetite in the elderly, a senior care specialist can offer the guidance and hands-on help needed.
Renewing Joy in Mealtimes for a Healthier Life
Helping seniors regain their appetite means understanding the unique blend of physical, emotional, and social factors that affect eating. Whether it’s incorporating food for the elderly with no appetite, adding supplements to increase appetite in the elderly, or exploring treatment for loss of appetite in the elderly, solutions are available and effective.
Westmont of Brentwood provides an enriching environment tailored to support healthy eating through social connections and expert care.
Contact us today at 925-516-8006 or schedule a tour to discover how we can support your loved one’s nutritional and emotional wellness.
Dive into the vibrant life our Westmont communities have to offer.Find Where You Belong
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my old person not feeling hungry?
Loss of appetite in the elderly can be caused by various factors such as changes in metabolism, reduced physical activity, certain medications, or underlying health conditions like depression or dementia. Aging naturally slows down digestion, which can lead to a feeling of fullness even with small meals. Dental problems or difficulty swallowing may also make eating less appealing. It’s important to monitor these changes and consult a healthcare provider if the loss of appetite persists.
How to naturally increase appetite in the elderly?
To naturally boost appetite in older adults, encourage regular light physical activity, which can stimulate hunger. Serving smaller, more frequent meals can also make eating less overwhelming. Use herbs and spices to enhance flavor without relying on salt, making meals more enjoyable. Creating a pleasant mealtime environment and eating with others can further improve interest in food.
What to eat to get your appetite back?
Eating easy-to-digest, nutrient-dense foods like soups, smoothies, and soft fruits can help reignite appetite. High-protein snacks like yogurt, boiled eggs, or peanut butter on toast offer both nutrition and energy. Incorporating bitter greens like arugula or citrus fruits before meals can stimulate digestion. Hydration is also key—drink plenty of water or herbal teas throughout the day.
What is the best appetite enhancer for seniors?
The best appetite enhancers for seniors often include natural solutions like ginger, ginseng, or vitamin B12 supplements, depending on nutritional needs. Prescription medications like megestrol acetate or mirtazapine may be recommended for severe cases, but only under medical supervision. Nutritional shakes and fortified snacks are convenient ways to supplement calorie intake. Always consult a doctor before starting any appetite stimulant to ensure it’s safe and effective for the individual’s condition.








