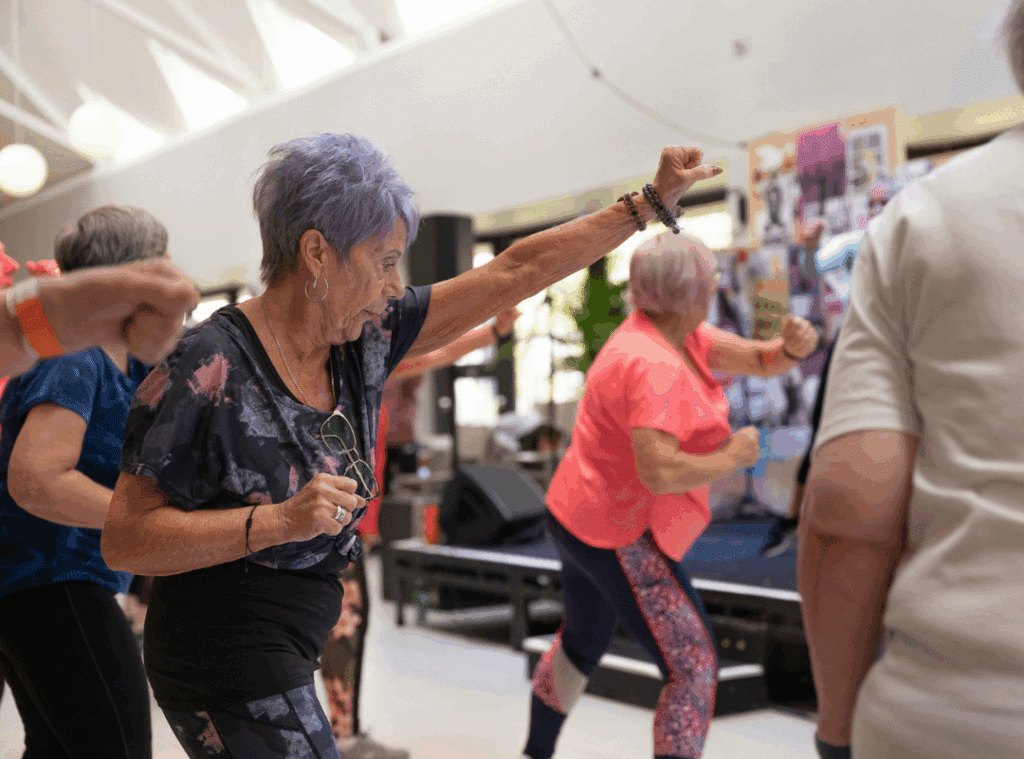Discover Retirement Living in Southern California
Retirement living in Southern California in 2026 is all about choice, comfort, and connection. Seniors today want more than just a place to live—they want a lifestyle that supports independence, encourages friendships, and brings peace of mind. From sunny weather to vibrant neighborhoods, this region remains one of the most popular destinations for retirees.
At Westmont of La Mesa, residents enjoy a welcoming environment designed to support daily life while celebrating individuality. With thoughtfully planned amenities, engaging activities, and a strong sense of community, retirement living in Southern California can genuinely feel like a fresh start rather than a slowdown.
Exploring Retirement Living Options in Southern California
Choosing among retirement homes in San Diego and nearby areas can feel overwhelming at first. Southern California offers a wide range of lifestyles, from quiet residential communities to socially active settings filled with events and programs. The key is finding a community that matches both your personal goals and your budget.
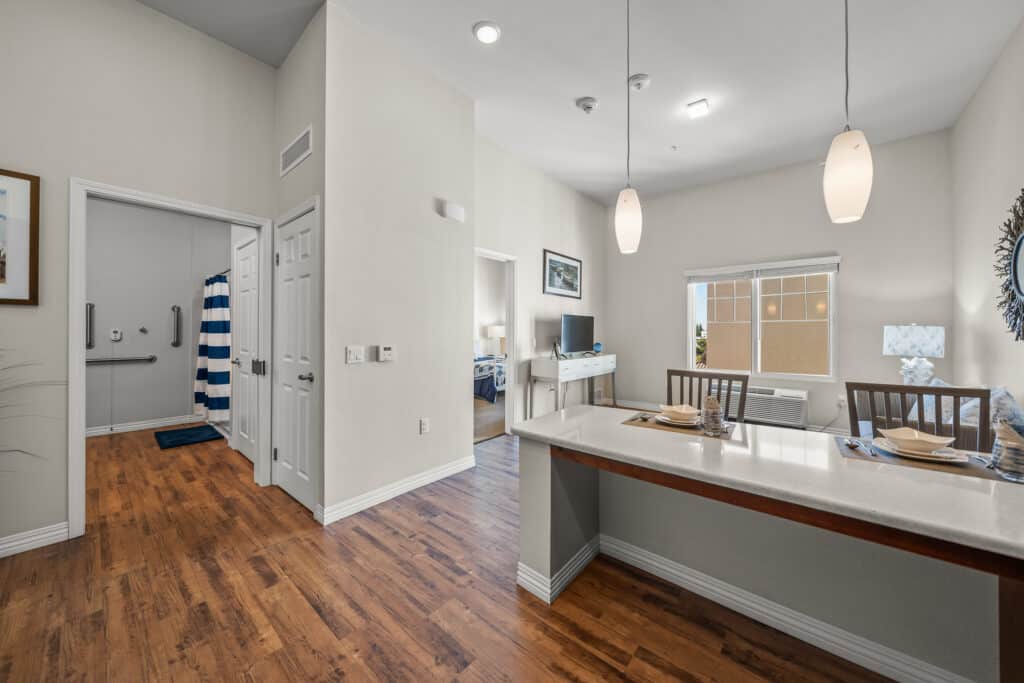
Understanding the cost of retirement living in Southern California is an important step. Costs can vary based on location, apartment size, and included services. That’s why touring communities, asking questions, and reviewing what’s included is essential. Communities like Westmont of La Mesa prioritize transparency and help families feel confident in their decisions.
When comparing communities, look closely at how residents spend their days. Do they have opportunities to socialize, stay active, and pursue hobbies they love? These details make a big difference in long-term happiness.
You may also want to explore insights from trusted sources like the National Institute on Aging, which explains senior housing options and offers planning tips. Learning more makes it easier to choose wisely.
Key Features to Look for in Retirement Communities
Community Amenities That Support Daily Life
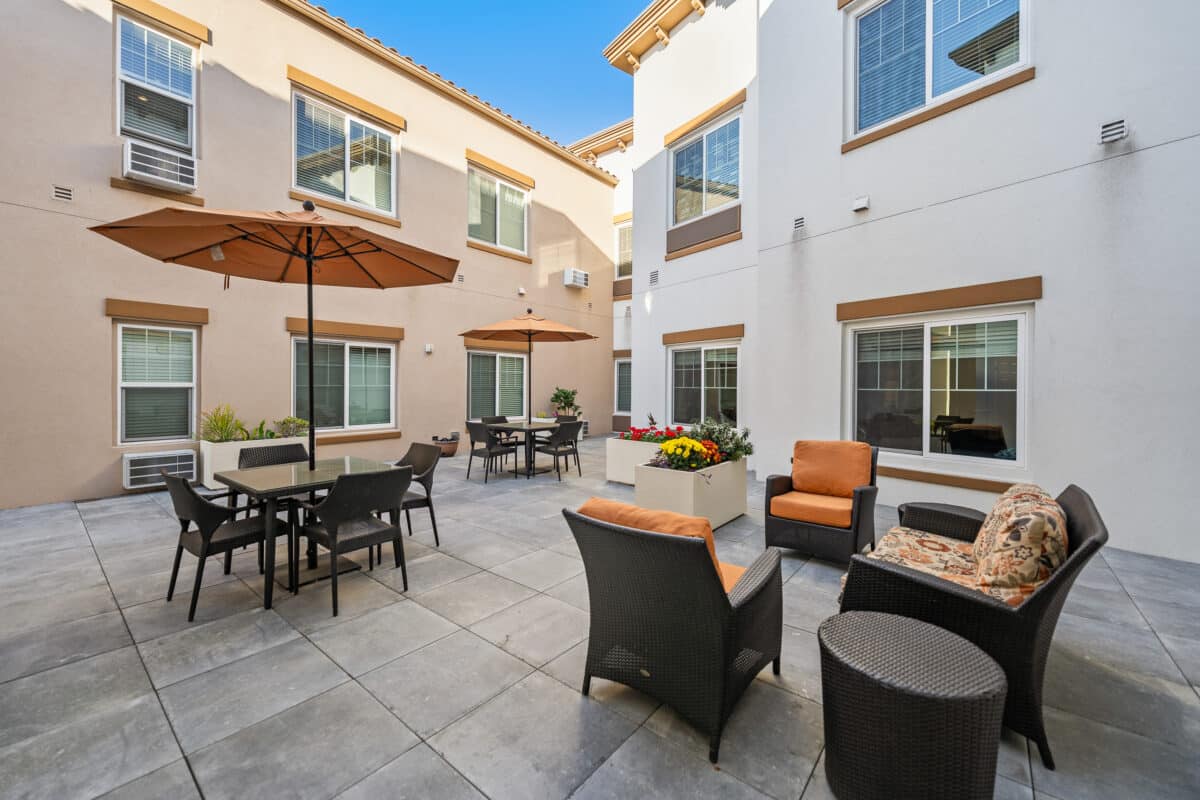
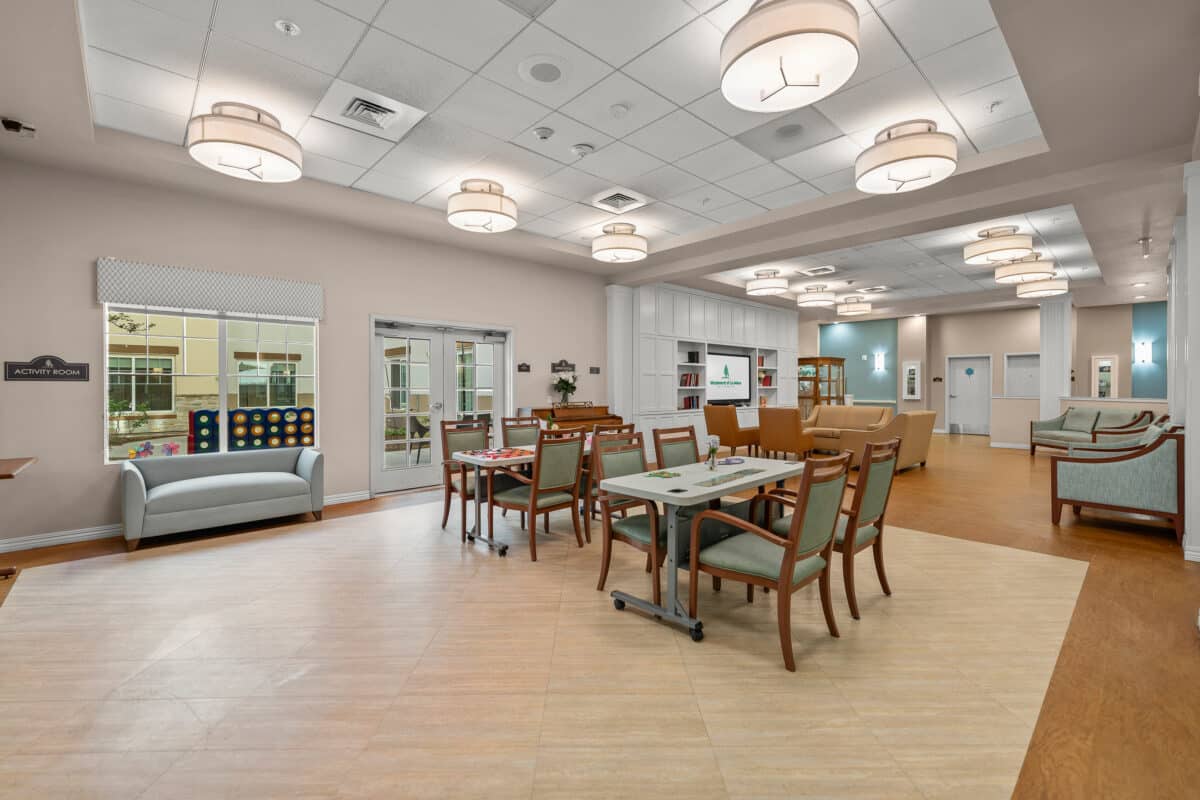
A strong retirement community supports both independence and connection. Look for amenities that encourage social interaction, movement, and creativity. Activity calendars, common gathering spaces, and wellness-focused programs help residents stay engaged.
Reading resident experiences can also be helpful. Testimonials often give insight into how the community feels day to day. At Westmont of La Mesa, the focus remains on comfort, dignity, and belonging—essential parts of independent retirement living that Southern California seniors appreciate.
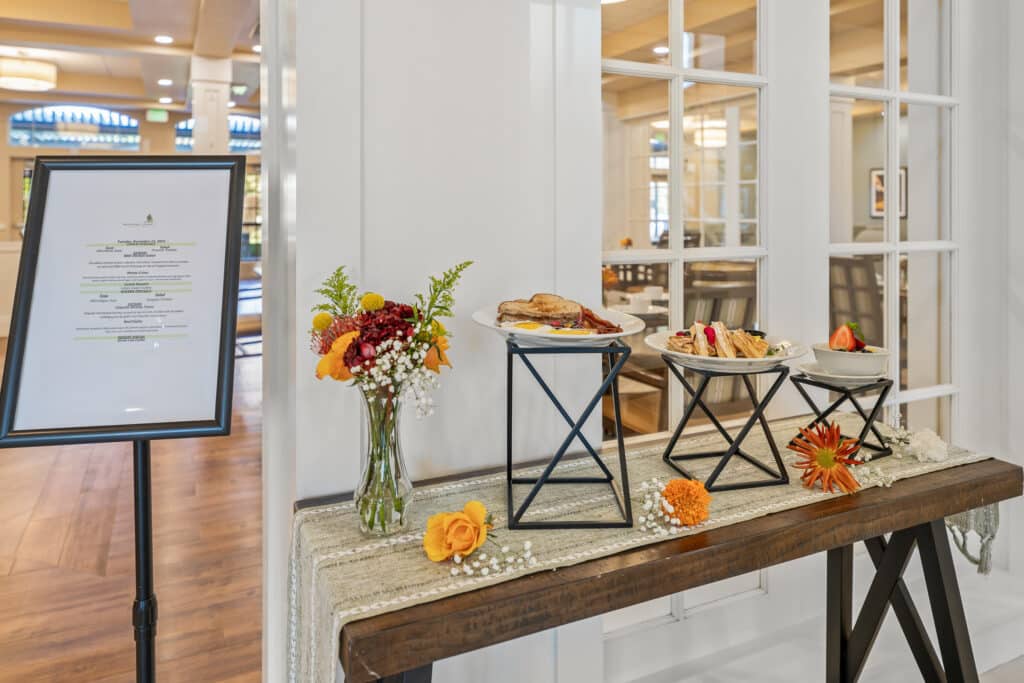
Dining is another key feature. Nutritious, chef-prepared meals enjoyed together help turn everyday dining into a social experience. You can also learn more about how thoughtful design enhances daily life by exploring this guide to senior living amenities.

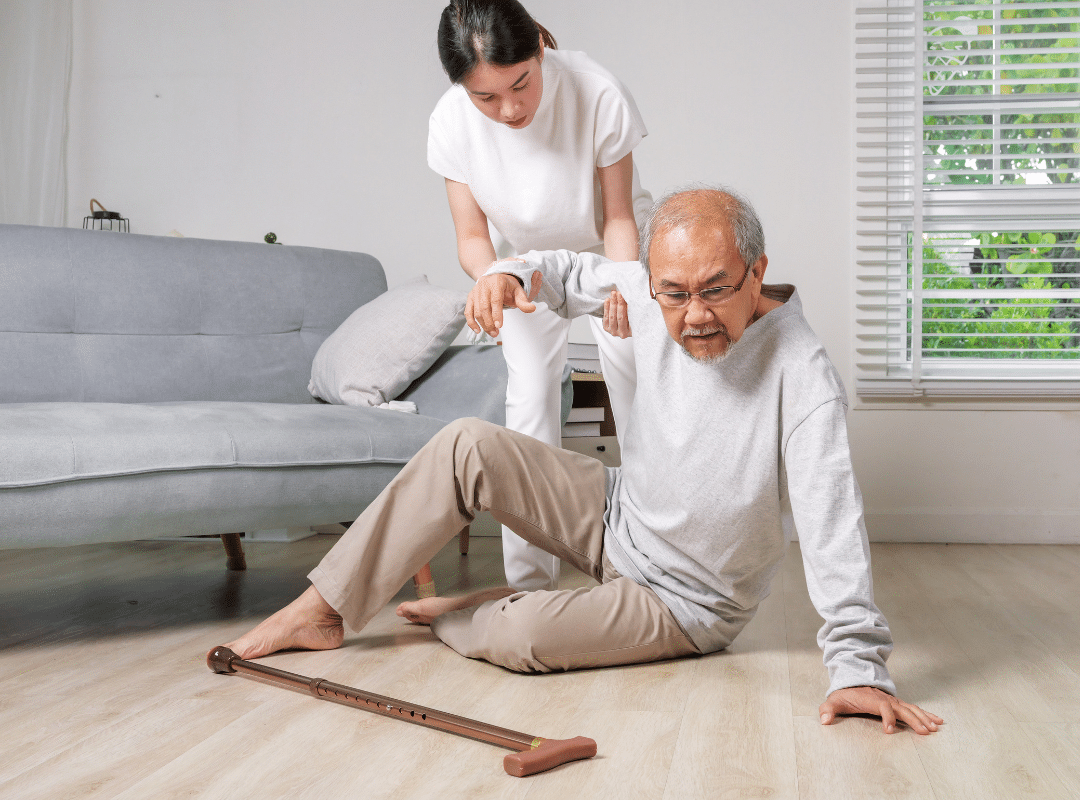
Why Safety and Security Matter in Retirement Living
Feeling safe allows residents to enjoy retirement living in Southern California without worry fully. A secure environment helps seniors focus on friendships, activities, and relaxation rather than daily concerns.
Retirement communities prioritize safety through trained staff, secure access points, and emergency systems. These features provide reassurance to both residents and their families.
Emergency Response Systems
Emergency response systems are an essential part of modern retirement homes in San Diego. In-apartment call systems allow residents to request help quickly when needed. Staff are trained to respond efficiently and calmly, creating confidence in the community’s readiness.
Communities also prepare for unexpected situations by coordinating with local healthcare providers. This approach ensures access to emergency medical services when necessary. You can learn more about this focus on preparedness through emergency medical access in assisted living.
Secure Living Environments
A secure community goes beyond locked doors. Well-lit hallways, thoughtful design, and staff availability all contribute to peace of mind. Knowing support is nearby allows residents to enjoy independence safely.
As needs change over time, it’s crucial to understand how communities adapt. Helpful guidance on this topic can be found in When Care Needs Increase in Independent Living, which explains how seniors can continue to feel supported.
The Role of Nutritious Dining in Retirement
Nutritious dining supports energy, health, and happiness. In luxury retirement living in Southern California, dining is often more than a meal—it’s a daily social highlight.
Shared meals encourage conversation and connection, turning neighbors into friends. Menus designed with balance and variety help residents maintain wellness while still enjoying delicious food. Dining together also helps reduce isolation, enriching community life and making it more enjoyable.
Benefits of Active Retirement Living
Active living is a cornerstone of independent retirement living that Southern California residents value. Staying active supports both physical and emotional well-being.
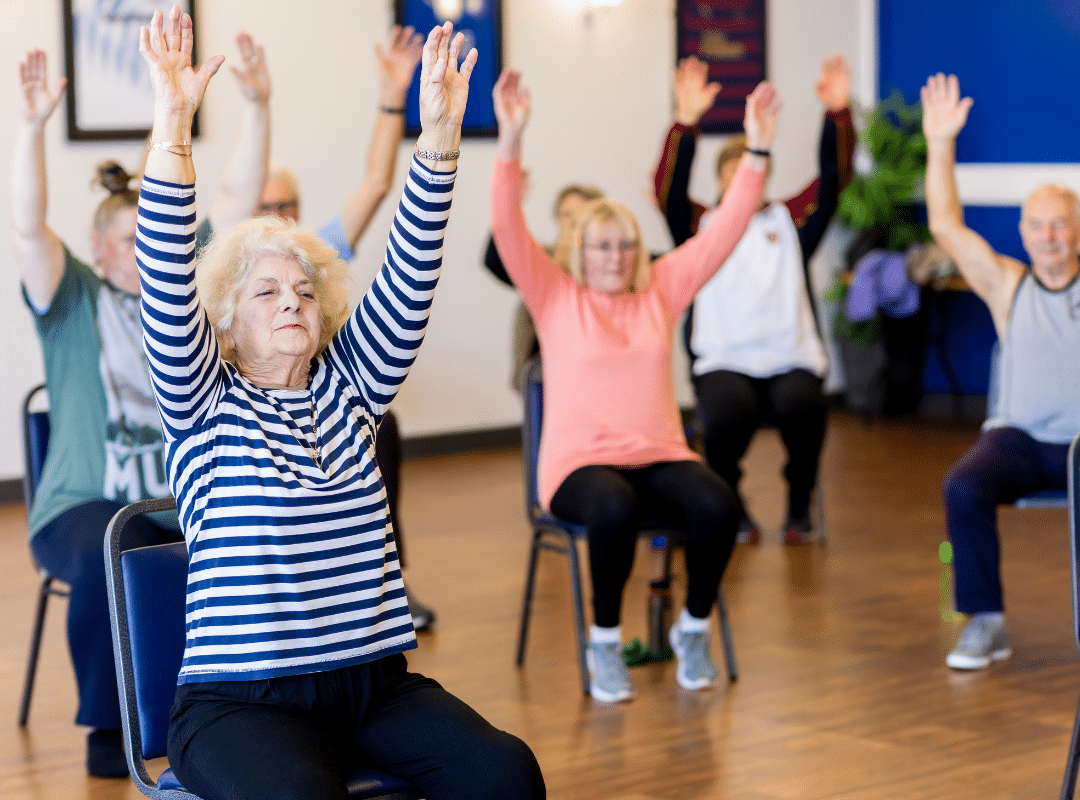
Stronger Social Connections
Social interaction is one of the most significant benefits of retirement living in Southern California. Group activities, shared meals, and community events help residents build meaningful relationships. These connections create a sense of belonging that makes every day brighter.
Better Physical Health
Movement supports long-term health at every age. Retirement communities that encourage gentle exercise, walking, and group fitness help residents stay mobile and confident. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, regular physical activity supports balance, heart health, and independence in older adults.
Mental Engagement and Lifelong Learning
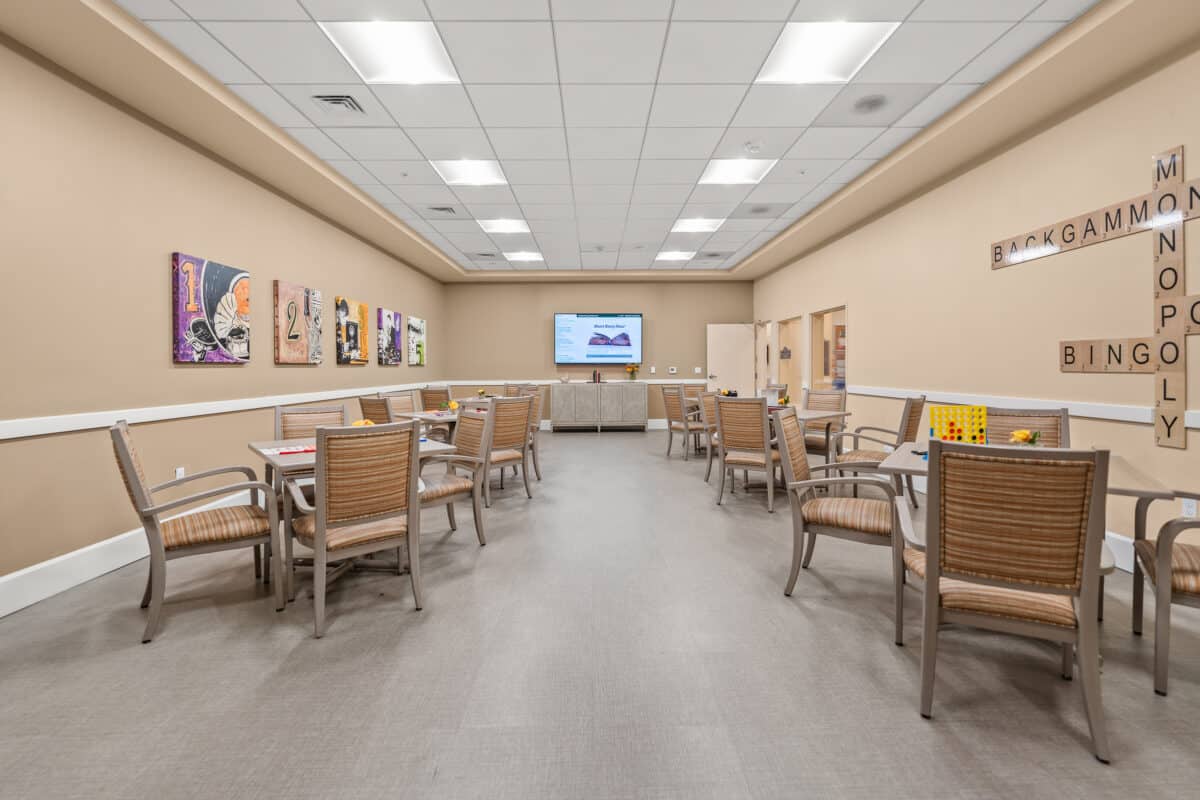
Mental stimulation is just as important as physical activity. Games, classes, and discussion groups keep minds sharp and spirits high. Engaging in lifelong learning helps residents stay curious and confident throughout retirement.
Cultural Activities That Enrich Retirement Life
Cultural activities add excitement and creativity to daily life. Many retirement homes in San Diego offer art programs, music events, guest speakers, and outings that connect residents with the broader community.
These experiences encourage self-expression and shared enjoyment. Whether attending a lecture or participating in a creative workshop, cultural activities bring variety and inspiration to retirement living.
Tips for Choosing the Right Retirement Community
Finding the right fit starts with understanding your priorities. Consider your desired lifestyle, social preferences, and budget. Reviewing the costs of retirement living in Southern California, along with included amenities, helps avoid surprises.
Visit communities when possible and talk with residents and staff. A welcoming atmosphere, friendly interactions, and clear communication are signs of a strong community. Choosing wisely ensures your retirement years feel comfortable and fulfilling.
Ready to Experience Retirement Living in Southern California? Call Today
Your next chapter should be filled with confidence, connection, and comfort. At Westmont of La Mesa, retirement living in Southern California is designed to help you enjoy each day with purpose and peace of mind. From engaging activities to supportive services, everything works together to support your lifestyle.
Now is the perfect time to explore your options. Call 619-369-9700 to speak with our team or schedule your personal visit today through Schedule a Tour. Your future community is waiting—let’s start the conversation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much money do you need to retire in Southern California?
The amount needed to retire in Southern California depends on your lifestyle, housing choice, and healthcare needs. Many retirees aim to save enough to cover annual living costs of $60,000 to $90,000 or more. Housing is typically the most significant expense, especially in coastal or metro areas. Planning for inflation, long-term care, and unexpected medical costs is also essential. A personalized retirement plan can help determine a more accurate target.
Where is the best place to live in California for retirees?
The best place to live in California for retirees depends on budget, climate preferences, and access to healthcare. Some retirees prefer coastal communities for mild weather, while others choose inland areas for more affordable housing. Access to senior services, public transportation, and recreational opportunities also plays a significant role. Communities with active senior lifestyles and supportive care options are often popular. Ultimately, the best location aligns with your financial and personal priorities.
How much is a retirement home per month in California?
The monthly cost of a retirement home in California typically ranges from $2,500 to over $6,000. Prices vary depending on location, level of care, and amenities offered. Independent living is usually more affordable than assisted living or memory care. Urban and coastal areas tend to have higher monthly rates. It’s essential to review which services are included to compare costs accurately.
Will Medicare pay for assisted living in California?
Medicare generally does not cover assisted living costs in California. It may pay for short-term medical services, such as rehabilitation or skilled nursing, but not for room and board. Some residents use Medicaid programs or long-term care insurance to help offset costs. Veterans’ benefits may also assist eligible individuals. Exploring all available financial options can help reduce out-of-pocket expenses.