Weak or tired legs can make it difficult for seniors to maintain independence, enjoy favorite activities, or even move safely around the house. Fortunately, there are proven solutions that can help restore strength, improve circulation, and rebuild confidence in daily mobility.
This guide explores the most effective treatments for weak legs in the elderly, including nutrition and supplements, targeted exercises, and medical options. Whether you’re experiencing gradual weakness or sudden weak legs in the elderly, you’ll find practical steps to recover safely and enhance your quality of life.
Causes and Symptoms of Leg Weakness in the Elderly
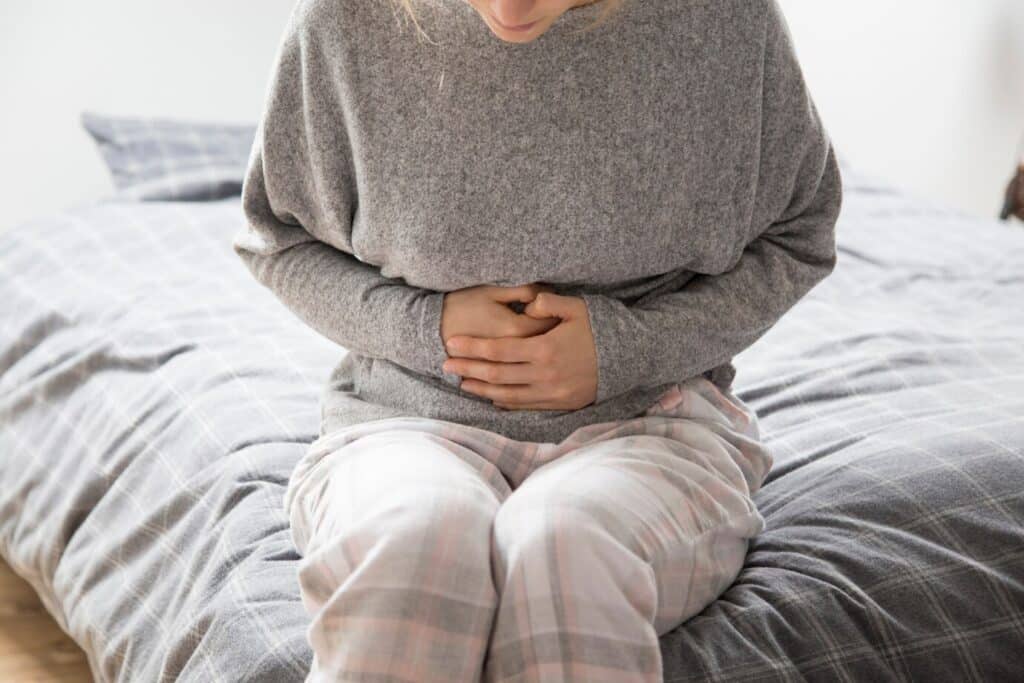
As people age, the muscles and nerves in their legs can weaken for several reasons. Common causes include poor circulation, nerve compression, and chronic conditions like diabetes or arthritis. Some may experience fatigue after short walks, while others may notice sudden weakness in the legs in the elderly, a warning sign that requires prompt medical attention.
Weak legs can also result from vitamin deficiencies or medication side effects. Symptoms often include trembling, numbness, or difficulty climbing stairs. These issues not only affect mobility but also increase fall risk. By identifying the underlying causes, seniors can receive the most suitable treatment for weak legs in the elderly, improving strength and stability over time.
Nutritional Support: What to Eat for Stronger Legs
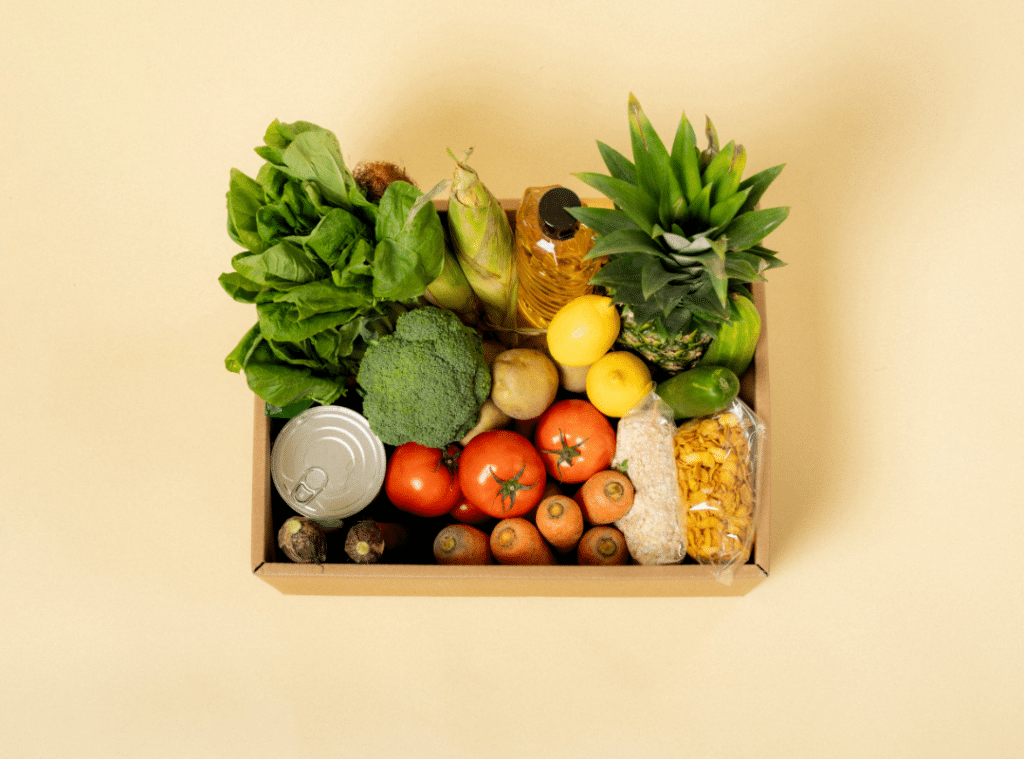
Proper nutrition plays a key role in any treatment for weak legs in the elderly. A balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and essential minerals supports muscle repair and nerve health.
What to Eat for Weak Legs in the Elderly
Knowing what to eat for weak legs in the elderly is crucial to rebuilding strength. Seniors should focus on:
- Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, eggs, and beans help repair muscle tissue
- Leafy greens and whole grains for improved circulation.
- Vitamin D and calcium-rich foods like dairy and fortified cereals help strengthen bones.
Hydration also supports muscle function. Dehydration can worsen fatigue and weakness. When seniors eat well, their muscles recover faster, and mobility improves naturally.
For more insights, check out Harvard Health’s guide on nutrition for seniors.
Additionally, good nutrition has been linked to longevity, vitality, and improved physical performance among older adults.

Helpful Supplements for Weak Legs in the Elderly
Even with a healthy diet, some nutrients can be difficult to obtain solely from food. In such cases, supplements for weak legs in the elderly can provide additional support.
Best Supplements for Weak Legs in the Elderly
- Vitamin D and calcium improve bone density and reduce fracture risk.
- Magnesium helps muscles relax and prevents cramps.
- Omega-3 fatty acids support circulation and heart health.
- B vitamins enhance nerve function and energy production.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting new supplements for weak legs in the elderly to avoid drug interactions or overuse. Proper supplementation, combined with a nutrient-dense diet, provides comprehensive treatment for weak legs in the elderly that targets root causes rather than symptoms.
For guidance on safe supplement use, review the National Institute on Aging’s recommendations.
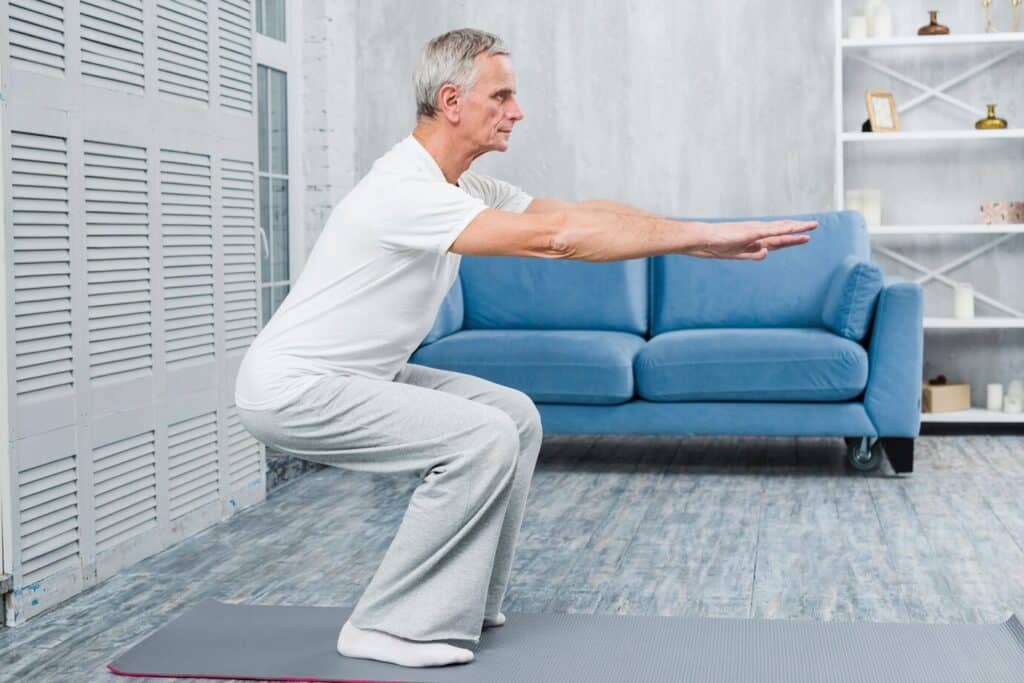
Effective Exercises for Weak Legs in Elderly Adults
Physical activity is one of the most potent ways to rebuild leg strength. A consistent fitness plan can help reverse muscle loss, improve balance, and reduce the risk of falls.
Exercises for Weak Legs in the Elderly
Start slow with exercises for weak legs in the elderly that are low-impact and easy on the joints:
- Seated leg raises and ankle rotations to enhance circulation.
- Mini squats and step-ups to build lower-body power.
- Walking and water aerobics to strengthen endurance safely.
Incorporating these exercises for weak legs in the elderly 2–3 times a week can noticeably improve coordination and mobility. Remember to stretch before and after workouts to prevent injury.
Adding empowering exercises to your daily routine helps seniors maintain flexibility, confidence, and overall well-being.

Medical Considerations and Professional Treatment Options
Sometimes, leg weakness stems from medical conditions requiring professional care. Consulting a doctor ensures a proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan for weak legs in elderly patients.
Common options include:
- Physical therapy: Personalized exercises that target specific muscle groups.
- Medication adjustments: Reviewing prescriptions that may cause weakness.
- Nerve pain medication for neuropathy-related issues.
- Muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatories to manage chronic discomfort.
| Cause | Medication Options | Recommended Actions |
| Nerve Damage | Nerve pain medications | Physical therapy |
| Muscle Weakness | Muscle relaxants | Strength training |
| Inflammation | Anti-inflammatory drugs | Regular monitoring |
A healthcare professional might also check for deficiencies that can cause sudden weakness in the legs in the elderly, such as low potassium or vitamin D levels. Additionally, non-drug methods like massage, hydrotherapy, and light stretching can complement medical treatment and enhance overall comfort.
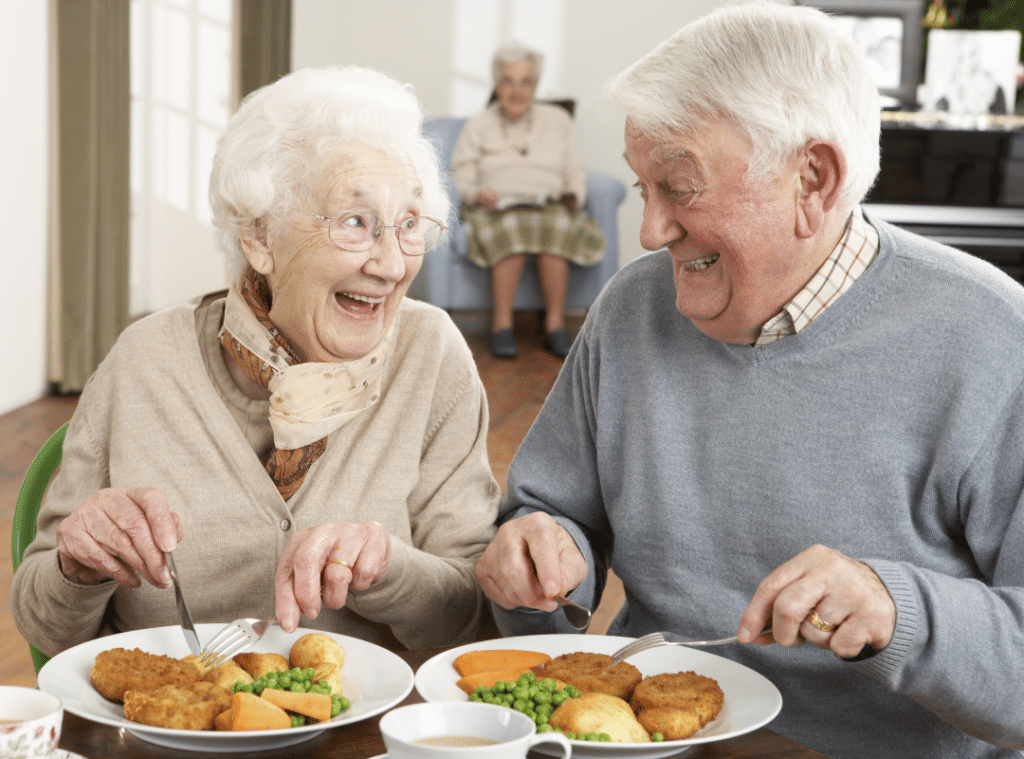
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Mobility and Independence
Building independence goes beyond diet and medication. Small lifestyle changes can significantly improve mobility and confidence.
- Use assistive devices like canes or walkers for support and safety.
- Practice balance exercises regularly to prevent falls.
- Stay active socially — joining group classes can motivate seniors to stay consistent with their fitness routines.
You can also follow leg exercises for seniors to maintain flexibility and strength. Simple daily habits, such as standing up every 30 minutes or walking short distances throughout the day, can keep circulation strong and muscles engaged.

Take the First Step Toward Stronger Legs Today
Regaining strength in your legs is not just about physical fitness, it’s about freedom, confidence, and quality of life. The right treatment for weak legs in the elderly combines balanced nutrition, targeted exercises, and safe supplements to rebuild strength over time. If you or your loved one experiences sudden weakness in the legs in the elderly, seek medical guidance immediately to prevent further complications.
At Westmont Living, we’re dedicated to helping seniors achieve healthier, stronger, and more active lives. Explore our communities, personalized wellness programs, and supportive care designed to meet every senior’s needs.
For more information, contact us today at 858-456-1233 or visit our website to learn how we can support your journey toward renewed strength and independence.
Compare The Costs of Senior Living vs Staying at Home
How Do The Costs Of Moving Into A Quality Senior Care Community Compare With The Costs Of Staying At Home?
Frequently Asked Questions
What would cause your legs to go weak?
Leg weakness can occur for various reasons, including muscle loss due to aging, nerve damage, poor circulation, or underlying medical conditions like diabetes or arthritis. It can also result from prolonged inactivity or vitamin deficiencies, particularly vitamin D or B12. In some cases, neurological issues such as stroke or Parkinson’s disease may contribute to weakness. Identifying the root cause through a medical evaluation is essential for proper treatment and prevention.
What is the best exercise for weak legs?
The best exercises for weak legs focus on improving strength, flexibility, and balance. Simple activities such as leg raises, seated marches, and squats help rebuild muscle strength. Walking, swimming, and light resistance training are also great options for seniors or individuals with limited mobility. It’s essential to start slowly and gradually increase intensity under the guidance of a professional to minimize the risk of injury.
Can the elderly regain leg strength in elderly?
Yes, elderly individuals can regain leg strength with regular exercise, proper nutrition, and medical support. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as strength training or balance exercises, helps rebuild muscle and improve mobility. A balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients also supports muscle recovery. With patience and persistence, many seniors see significant improvement in strength and independence.
What medication is good for leg weakness?
Medications for leg weakness depend on the underlying cause. For instance, doctors may prescribe supplements to address vitamin deficiencies, anti-inflammatory drugs for arthritis, or medications to improve blood flow for circulation issues. If the weakness is related to nerve damage, treatments may include medicines for nerve pain or physical therapy. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your condition.