How to Manage Diabetes in Seniors Effectively
Managing diabetes in seniors requires more than just routine check-ups—it’s a lifestyle shift supported by knowledge, vigilance, and compassionate care. At Lakeview Senior Living in Lincoln City, OR, we understand that aging brings unique health challenges, and diabetes is among the most common. Roughly one in three individuals over 65 lives with diabetes. That’s why understanding the condition and taking a personalized approach is essential. Everything from balanced nutrition and physical activity to emotional support and regular screenings plays a role. Awareness of what to watch for—like the first signs of diabetes in seniors—and how to act early can make a life-changing difference. It’s not about restriction; it’s about living well and confidently. Keep reading to learn how you or your loved one can take control of diabetes and age with vitality.
What Are the First Signs of Diabetes in Seniors?
Early detection is crucial when managing diabetes in seniors. Often, the initial symptoms are subtle and mistaken for signs of aging. However, recognizing these early changes can help prevent more serious complications. Some of the first signs of diabetes in seniors include frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. In particular, these indicators can be more pronounced in women. Knowing the symptoms of diabetes in elderly women, such as recurring infections or slow-healing wounds, is equally important.
Understanding these signs ensures that seniors or their caregivers can seek medical attention promptly. Left unchecked, blood sugar levels can climb and cause diabetes, complications in the elderly, such as nerve damage, kidney issues, or vision problems. Keeping a watchful eye on your health is the first step in taking control.
How to Avoid Diabetes in Old Age Through Lifestyle Choices
Preventing diabetes is possible with simple, mindful changes. Knowing how to avoid diabetes in old age starts with prioritizing your diet. Stick to meals with whole grains, lean proteins, and colorful vegetables. Reducing processed sugar and keeping portion sizes in check also helps maintain stable blood glucose levels.
Physical activity plays a huge role. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate movement each week, like walking or swimming. It’s not about intensity but consistency. To make movement fun and social, try incorporating small group activities for nursing home residents, such as dance classes or yoga sessions. Mental health also matters—managing stress reduces the risk of high blood sugar spikes and promotes better well-being.
Diabetes in the Elderly Guidelines for Care
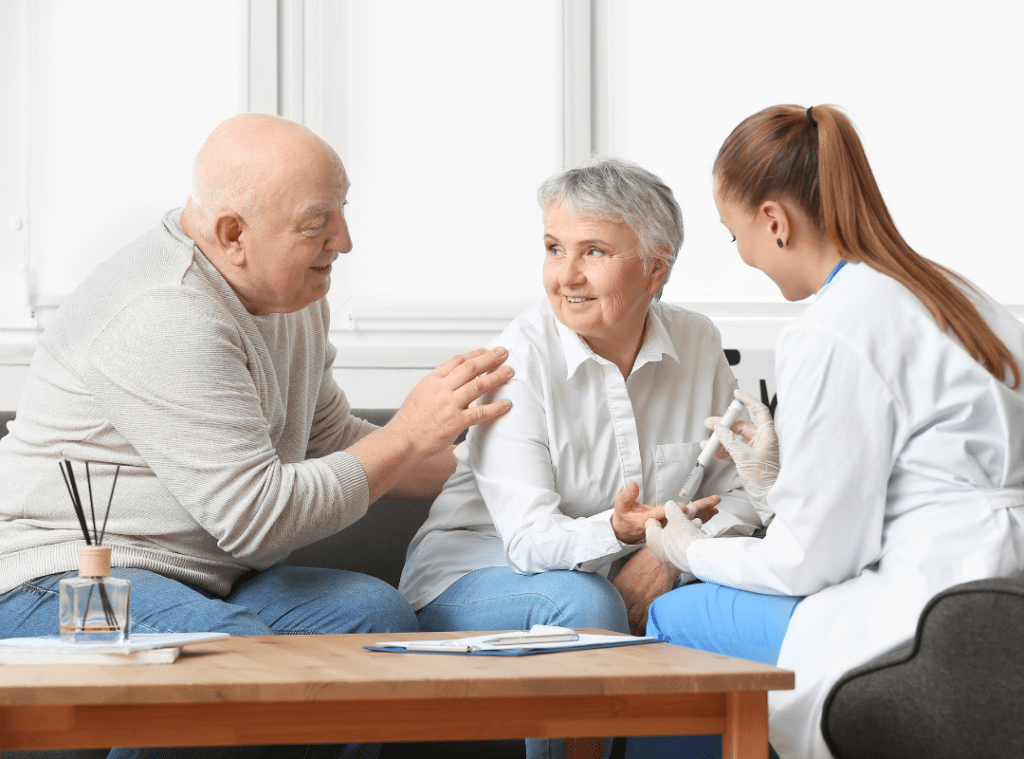
Healthcare professionals follow clear diabetes guidelines for the elderly to manage the condition effectively. These guidelines emphasize an individualized approach, where treatment is based on a senior’s physical ability, cognitive function, and lifestyle. Regular health screenings are a core part of this process.
Doctors typically recommend frequent blood sugar monitoring, tailored diet plans, and scheduled exercise routines. With support, these strategies are easier to follow for seniors, especially those in assisted living. Consider meals designed with diabetes-friendly ingredients or care teams that provide daily activity plans. At Lakeview Senior Living, we strive to create a supportive environment where managing diabetes doesn’t feel like a burden—it becomes a lifestyle.
Preventing Diabetes, Elderly Complications
The risk of diabetes and elderly complications increases with age, but preventative care can make all the difference. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to nerve pain, poor circulation, kidney issues, or even cognitive decline. To prevent this, seniors should schedule regular visits with their care team, stick to their medication schedules, and stay hydrated.
Another way to reduce the risk of complications is to focus on nutrient-dense meals and track how different foods affect blood sugar levels. Dietitians often recommend incorporating fiber-rich foods and lean proteins into daily meals, as these promote better glycemic control. Monitoring doesn’t stop at glucose—it also includes blood pressure, cholesterol, and kidney function. All these elements work together to manage long-term health.
Support Systems That Make a Difference
Diabetes isn’t a solitary journey, and having a network of support significantly improves outcomes. Whether it’s a group exercise class or a shared meal, small group activities for nursing home residents can spark motivation and improve health. These environments promote physical movement, emotional connection, and accountability.
Online forums and support groups provide a space to exchange tips, discuss challenges, and find emotional encouragement. Plus, healthcare providers and certified diabetes educators offer personalized strategies and solutions for managing the condition. For additional help, check out the benefits of health screenings in assisted living, which identify issues before they escalate.
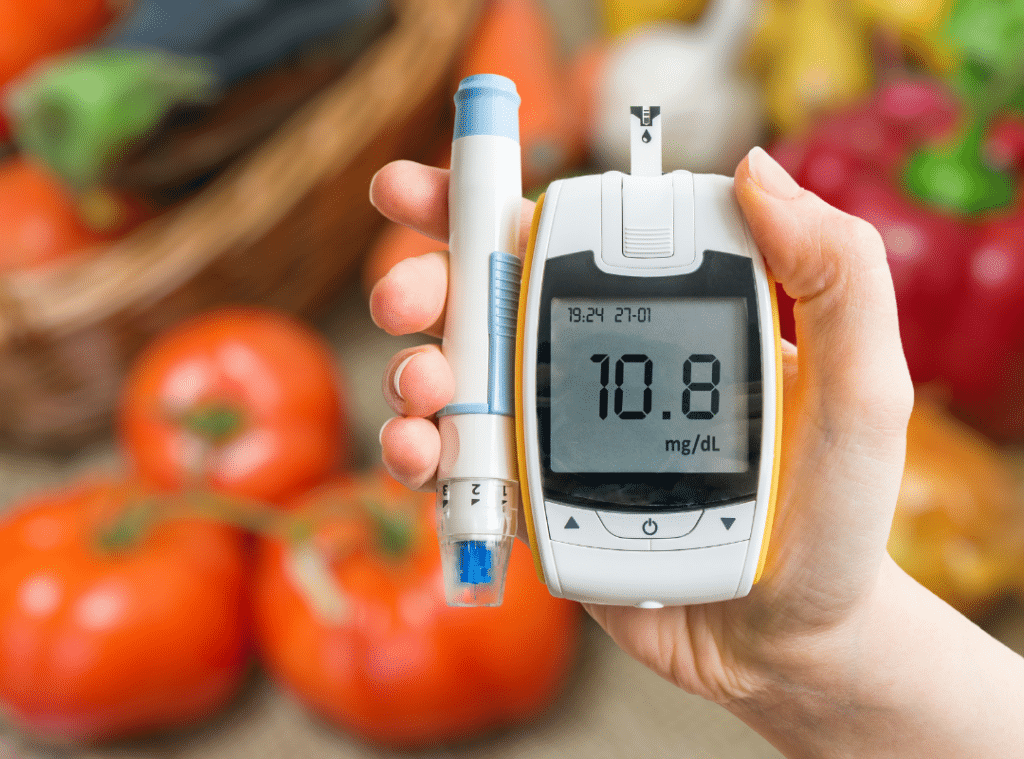
Monitoring and Managing Long-Term Health
Monitoring is the foundation of diabetes care. For seniors, this means keeping track of glucose and the broader picture of wellness. From eye exams to kidney checks, managing chronic illness requires full-body awareness. Make monitoring a habit, not a chore.
Using apps, journals, or caregiver support can simplify this task. Regular assessments help ensure that treatment plans are working. They also allow caregivers and doctors to adjust medications or habits when needed. At Lakeview Senior Living, we encourage ongoing conversations between residents and care teams to stay ahead of changes and maintain confidence in their health plan.
Taking a proactive stance with support, education, and consistent care can reduce risks and promote longevity. Remember, you’re not alone in this. If you’re looking for compassionate care and expert guidance, call Lakeview Senior Living today at 541-994-7400. Let’s build a future of strength and wellness together.
Discover the level of care you or your family member requires. What Level of Care Do You Need?
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of diabetes in the elderly?
In older adults, common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. However, confusion, weight loss, or urinary incontinence may be subtle and mistaken for normal aging. Monitoring these changes and consulting a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis is essential. Early detection can help manage the condition more effectively.
What are the 4 stages of diabetes?
The four stages of diabetes progression include:
- Insulin resistance – when the body becomes less responsive to insulin.
- Prediabetes – blood sugar levels are elevated but not yet high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
- Type 2 diabetes – consistent high blood sugar due to poor insulin response or production.
- Diabetes complications – damage to organs and systems, such as the heart, kidneys, and nerves. Early management can slow or prevent progression between stages.
What is the life expectancy of a diabetic person at 65?
Life expectancy for a 65-year-old with diabetes varies depending on how well the condition is managed. With reasonable blood sugar control, a healthy lifestyle, and regular medical care, many people live well into their 70s, 80s, or beyond. However, unmanaged diabetes can lead to serious complications that may shorten lifespan. Personalized medical care plays a key role in improving outcomes.
How do you treat diabetes in the elderly
Treating diabetes in older adults often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and blood sugar monitoring are essential. Depending on the individual’s health and needs, doctors may prescribe oral medications or insulin. Care plans are usually tailored to minimize risks like low blood sugar and to account for other age-related conditions.








