How Do Nutritional Needs Change Over Time? A Lifespan Guide
Steering the journey of life often requires a little fine-tuning when it comes to nutrition. At Lakeview Senior Living, we understand that your dietary needs shift as you move from infancy to old age, with each stage presenting unique challenges and requirements. From the nutrient-dense demands of early development to the more nuanced needs of older adulthood, understanding these changes is vital for maintaining health. So, how can you guarantee your diet evolves in harmony with your age? Let’s explore the key nutritional milestones along the way with Lakeview Senior Living.
How nutritional needs change over time
As you progress through life, your nutritional needs shift considerably across various stages. Infants require high levels of nutrients for rapid growth, relying on breastfeeding or formula.
As children, the focus shifts to a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support ongoing development. During adolescence, your body demands more calcium and iron, especially for females experiencing menstruation.
Entering adulthood, your nutritional needs become influenced by lifestyle factors, such as pregnancy or physical activity. It’s important to maintain a balanced intake to support overall health.
As you age, your requirements change again; older adults typically need fewer calories but higher amounts of certain nutrients, including protein, calcium, and vitamin D. Proper nutrition is essential for senior health and well-being.
With aging, your body may struggle to absorb nutrients effectively, so being proactive about your diet is necessary. Decreased appetite and hydration sensitivity can complicate matters, making it essential to prioritize nutrient-dense foods and regular hydration.
Throughout these changes, understanding and adapting to your changing nutritional needs can help you maintain health and wellness, allowing you to serve others with vitality and vigor.
Nutritional needs at different stages of life
Nutritional needs vary considerably at each stage of life, and understanding these changes can help you make informed dietary choices.
For infants and toddlers, focus on providing nutrient-dense foods, as their needs are high relative to body weight. Healthy fats should make up 30-40% of their caloric intake, supporting brain development.
As children grow, their caloric needs shift with age and activity. Encourage a variety of whole foods to prevent reliance on empty calories.
Nutrients like calcium and iron become essential for teens and young adults, especially for females, due to menstruation. Establishing healthy eating habits now can set a foundation for life.
In adulthood, nutritional needs fluctuate based on lifestyle changes and health conditions. Pregnant women, for instance, require additional calories and key nutrients.
As you age, your body may demand fewer calories but higher nutrient density, particularly for calcium and vitamin D to maintain bone health. Personalized nutrition is also important to cater to specific dietary needs in later life.
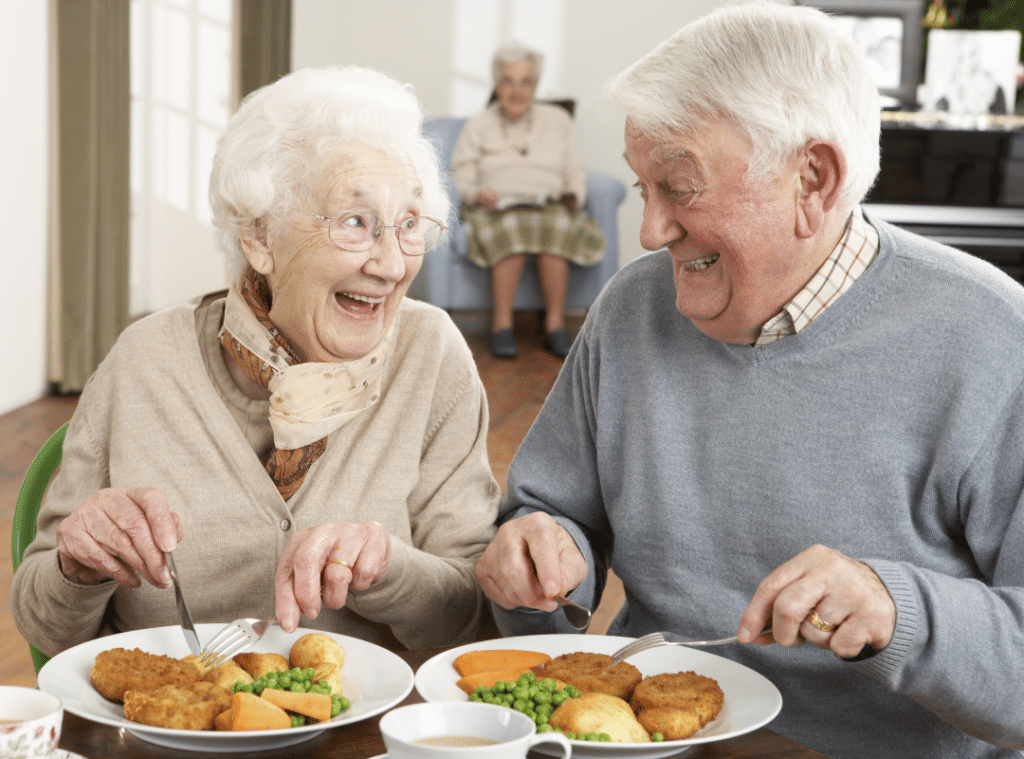
Nutrition for elderly
Understanding nutrition for the elderly is essential, especially since their dietary needs shift considerably as they age. As you care for elderly individuals, focus on nutrient density rather than caloric intake. Key nutrients include protein, vitamin D, calcium, and B12, critical for maintaining health. Good nutrition can significantly reduce chronic disease risk and improve overall well-being.
| Nutrient | Importance | Sources |
| Protein | Supports muscle maintenance and reduces sarcopenia | Lean meats, fish, legumes |
| Vitamin D | Aids calcium absorption for bone health | Fatty fish, fortified milk |
| Calcium | Essential for bone strength | Dairy products, leafy greens |
| Vitamin B12 | Important for nerve function and red blood cells | Meat, dairy, fortified cereals |
| Fiber | Promotes digestive health and prevents constipation | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains |
Older adults may experience diminished appetite and hydration challenges, making it important to encourage regular fluid intake and smaller, nutrient-rich meals. Regular health assessments can help tailor dietary plans, ensuring that nutritional needs are met effectively. By focusing on these aspects, you can greatly enhance the quality of life for the elderly individuals in your care.
Nutrition for older adults
Maintaining a balanced diet is essential for older adults, as their nutritional needs change considerably with age.
As you age, it’s vital to focus on nutrient-dense foods that meet your body’s requirements while combating common deficiencies. Here are three key areas to take into account:
- Protein Intake: Aim for high-protein foods to help preserve muscle mass. Lean meats, fish, legumes, and dairy can be excellent sources.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day. Dehydration can lead to serious health issues, so make it a habit to keep water or herbal teas nearby.
- Vitamin D and Calcium: Prioritize foods rich in these nutrients for bone health. Think about fortified foods or supplements if dietary sources are insufficient. Additionally, incorporating fiber-rich foods can improve digestion and overall health, which is particularly important as you age.
Nutritional needs
As you age, your body’s nutritional needs evolve considerably, making it essential to adapt your diet accordingly. You might notice changes in appetite, digestion, and nutrient absorption, all of which impact your overall health.
For instance, as muscle mass declines, your protein intake becomes increasingly important to preserve strength and prevent sarcopenia. Aim for a variety of protein sources, including lean meats, legumes, and dairy.
You also need more calcium and vitamin D to support bone health, especially since your ability to absorb these nutrients decreases with age. Incorporating foods like leafy greens and fatty fish can help meet these requirements.
Additionally, don’t overlook hydration; as thirst signals diminish, it’s essential to consciously drink water throughout the day to avoid dehydration.
Be aware that nutrient deficiencies, particularly in vitamin B12 and magnesium, are common in older adults. Regular health check-ups can help you monitor and adjust your dietary intake.
How does age affect nutritional needs?
Nutritional needs change considerably as you age, influenced by various physiological factors.
As you grow older, your body undergoes changes that can affect everything from appetite to nutrient absorption, making it essential to adapt your diet accordingly.
Here are three key ways age impacts your nutritional needs:
- Caloric Needs Decrease: With reduced muscle mass and lower activity levels, you generally require fewer calories.
This makes it important to focus on nutrient-dense foods to meet your needs without excessive calories.
- Protein Intake is essential: You lose muscle mass at a rate of 3–8% per decade after age 30.
Increasing protein intake can help combat this loss and support muscle health.
- Hydration Awareness: Aging diminishes your sensitivity to hunger and thirst, raising the risk of dehydration.
Drinking enough fluids is critical for maintaining overall health.

Adulthood dietary needs
During adulthood, your dietary needs evolve considerably due to various lifestyle factors, such as changes in activity levels, metabolism, and life events like pregnancy or menopause.
You’ll need to focus on a balanced intake of essential nutrients to support your overall health and well-being. Protein becomes particularly important as you age, especially if you’re involved in physical activities or looking to maintain muscle mass. Aim for lean sources, like chicken, fish, beans, and legumes.
Additionally, ensure you’re getting enough calcium and vitamin D to support your bone health, especially if you’re a woman experiencing menopause. Be mindful of your hydration, as many adults don’t drink enough water throughout the day.
Incorporating fruits and vegetables can help meet both hydration and nutrient needs. Regularly consuming whole grains and healthy fats will contribute to a well-rounded diet.
Lastly, consider how life events impact your nutritional requirements. For instance, pregnancy demands more calories and nutrients, while aging may reduce your caloric needs.
Assess your dietary habits regularly and consult healthcare professionals to adapt your nutrition according to your life stage. This will ensure that you nourish both yourself and those you care for.
Life cycle definition in foods
Understanding the life cycle definition in foods helps you appreciate how individuals’ nutritional needs can shift throughout different stages of life.
The life cycle of food refers to the journey from production to consumption, emphasizing how dietary requirements evolve with age.
Here’s what you need to reflect on:
- Infants and Toddlers: There are high nutrient demands for rapid growth, and breastfeeding or formula is essential in the first year.
- Adolescents: Due to growth spurts, adolescents have increased needs for calcium and iron; establishing healthy eating habits is critical for lifelong wellness.
- Older Adults: Focus shifts to nutrient density; essential nutrients like protein, calcium, and vitamins become important for sustaining health and preventing deficiencies.
As you navigate the intricate tapestry of life, your nutritional needs shift like the changing seasons. From the vibrant growth of infancy to the wise choices of adulthood and the nutrient-dense needs of older age, each stage requires a tailored approach to diet. Staying mindful of these evolving requirements guarantees you’re surviving and thriving. Regularly evaluating your nutritional intake can cultivate a healthier, more vibrant life at every age.
At Lakeview Senior Living, we understand the importance of proper nutrition for all life stages. For more information or assistance with your dietary needs, please contact us at 541-994-7400.
Discover the level of care you or your family member requires. What Level of Care Do You Need?
Questions on Nutritional Needs
- How do nutritional needs change, including the number of calories?
Nutritional needs evolve with age due to metabolism, activity levels, and body composition changes. Individuals’ calorie requirements generally decrease as they age, but their need for nutrient-dense foods increases to maintain health and prevent chronic conditions. - How do nutritional needs change in young adulthood?
In young adulthood, the body requires more calories and nutrients to support physical activity, muscle maintenance, and overall growth. As people transition to middle and older adulthood, their metabolism slows, and they may need fewer calories but more vitamins, minerals, and protein to preserve health. - Which group requires a caloric intake range of 1800–2400 calories daily?
Women in the general adult population typically require 1,800–2,400 calories daily, depending on their age, activity level, and overall health. Active individuals or younger adults in this group may need calories on the higher end of this range.








